We all know traditional barcodes—the familiar black-and-white lines that we find in retail and inventory management. They efficiently store product information and speed up transactions at the checkout by leveraging a barcode scanner. But as technology advances, so do barcode systems.
2D barcodes are a significant upgrade on the basic concept of a barcode. Unlike their one-dimensional predecessors, 2D barcodes can store vast amounts of data in a compact, scannable format, opening up a world of possibilities for businesses and consumers alike.
From tracking inventory with precision to enabling seamless mobile payments, 2D barcodes are becoming an integral part of the digital landscape. Let’s explore what sets them apart from traditional barcodes and how you can start using them to your advantage.
Table of Contents
- What Are 2D Barcodes?
- What are the differences between 1D and 2D barcodes?
- How Can 2D Barcodes Be Used?
- What Are the Advantages of 2D Barcodes?
- Wrap-Up
What Are 2D Barcodes?
The 2D barcode —or two-dimensional barcodes— is a type of code that can encode data, both horizontally and vertically. This two-dimensional structure allows 2D barcodes to store a great deal of information in a small space, which can be accessed through barcode scanners. Main features include:
High data capacity: 2D barcodes can store significantly more data than 1D barcodes. While 1D barcodes typically store around 20–25 characters, 2D barcodes can store up to several thousand characters, including text, URLs, and even small images.
Structure: They are usually square or rectangular and consist of small black and white squares, dots, or other geometric patterns arranged in a grid. The data is encoded in both the horizontal and vertical dimensions.
Error correction: Many 2D barcodes include error correction, allowing the barcode to be read accurately even if it’s partially damaged or obscured. This makes them more reliable in environments where barcodes might get damaged.
Types of 2D barcodes
Data matrix codes
This type of 2D barcode is known for its high data density and compact size. It is particularly effective for marking small items and is widely used in industries that require tracking and identification of products where space for labeling is limited.
They are composed of black and white cells (dots) arranged in a square or rectangular grid. The code has a unique “L-shaped” finder pattern along two adjacent edges, which helps barcode scanners determine the orientation of the code. The remaining two sides of the code have a dotted border, which defines the data area and aids in scanning.
A Data Matrix code can store up to around 2,335 alphanumeric characters or 1,556 bytes of binary data. It is widely used in manufacturing to mark small parts and components, particularly in the electronics and automotive industries.
In the healthcare sector, Data Matrix codes are used on medical devices, surgical instruments, and medication packaging. They ensure accurate tracking and traceability, which is critical for patient safety and regulatory compliance.
QR codes

The Quick Response Code is perhaps the most recognized 2D barcode. There are QR codes for marketing, payments, and linking to websites. You can scan a QR code with most mobile phones, making them highly accessible and capable of offering fast data access.
QR codes are square-shaped with a grid of black and white squares. They include three distinctive square patterns, known as “finder patterns,” located in three corners of the code. These patterns help scanners detect the code’s orientation and accurately read it from any angle.
The remaining area of the QR code is filled with data and error correction patterns.
QR codes can store up to approximately 4,296 alphanumeric characters or 2,953 bytes of binary data. They can also encode special characters, such as Kanji characters, making them versatile for various languages and data types.
PDF417 codes

PDF417 is a type of 2D barcode that is widely used for encoding large amounts of data in a compact format. The name “PDF417” comes from “Portable Data File” and the fact that each pattern in the code is made up of 4 bars and spaces, each of which is 17 units long.
They’re mostly used for identification documents like driver’s licenses, passports, and other forms of identification to store personal details, such as name, address, and license number. This allows for quick and secure verification of identity.
Many airline boarding passes and train tickets use PDF417 codes to store flight or travel information, including passenger names, seat numbers, and boarding times.
PDF417 is also used for tracking packages and pallets in supply chains, as it can store detailed shipping information in a small space.
Aztec code
This type of 2D barcode is known for its high data capacity and robust error correction capabilities. It is designed to be compact and versatile, making it suitable for various applications where space is limited and reliability is crucial.
Aztec codes are square in shape and consist of a grid of black and white squares arranged in a specific pattern. They include a central “bullseye” pattern, which helps scanners locate and orient the code, similar to the finder patterns in QR codes.
Aztec codes can store up to approximately 3,120 alphanumeric characters or 1,905 bytes of binary data. They can be quite compact, which allows them to be used in situations where space is limited. They are typically used in small labels or tags, or airline boarding passes, train tickets, and other travel documents.
Some mobile payment systems use Aztec codes to store payment information. Scanning an Aztec code at a point-of-sale terminal can quickly complete a transaction.
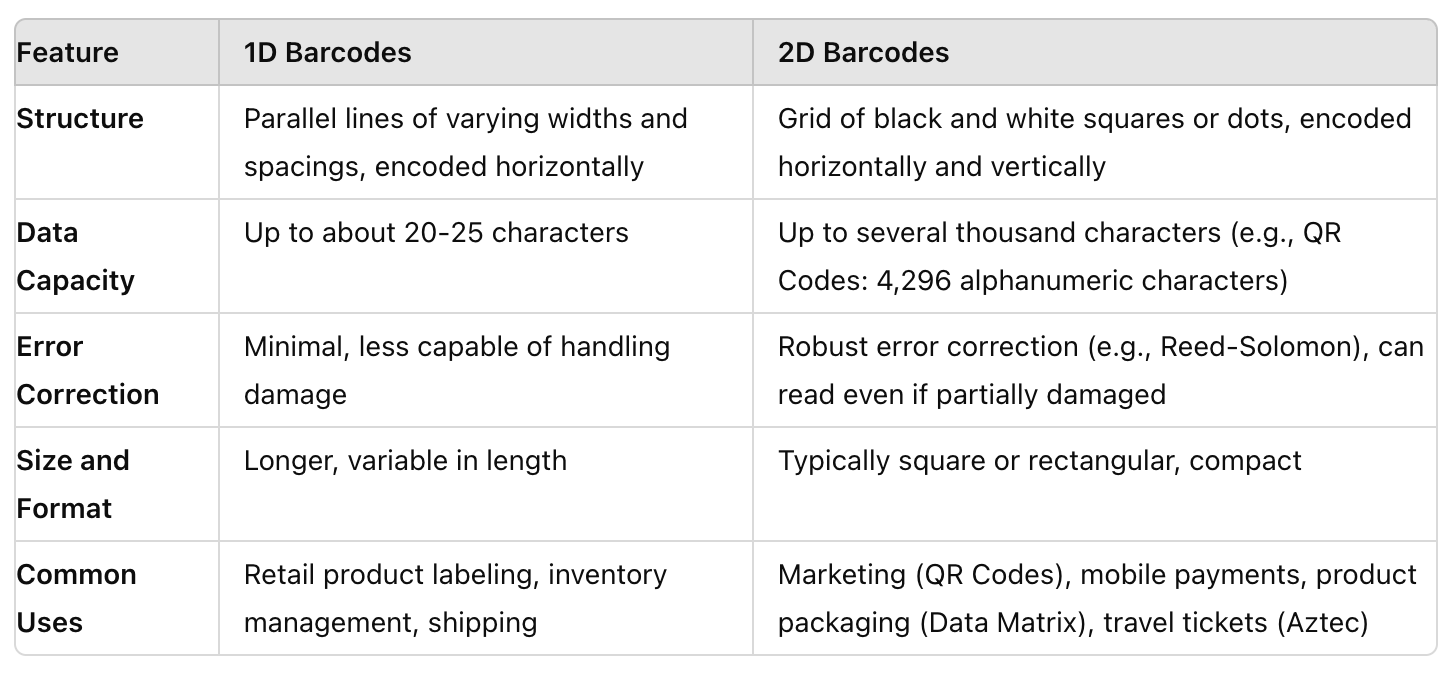
What are the differences between 1D and 2D barcodes?
1D are linear barcodes and are also used for encoding data in a visual format that can be scanned and read by scanners. However, they differ significantly in their structure, encoded data capacity, and applications from 2d codes. Here’s a comparison of the two:
How Can 2D Barcodes Be Used?
2D barcodes offer a versatile range of applications due to their ability to store large amounts of data in a compact form. Here are some common and innovative ways 2D barcodes can be used:
Marketing and advertising
Companies use 2D codes on product packaging that link to detailed product information, reviews, and usage instructions. They also use them to offer special promotions, discounts, or digital coupons that customers can access by scanning the code.
QR codes, in particular, can direct users to interactive content such as videos, surveys, or social media campaigns.
Mobile payments
Today, retailers, banks, and other businesses use 2D codes in mobile payment systems, allowing users to complete transactions by scanning a code at the point of sale. They can be integrated into digital wallets for easy access to payment methods and transaction history.
Product tracking and authenticity

Data Matrix codes can be used for tracking products through the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and reducing counterfeiting. They often integrate with a Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) to provide a comprehensive system for product identification and verification.
Data matrix codes help in managing and tracking inventory, making it easier to monitor stock levels and locations.
Healthcare industry
QR codes on patient wristbands can store vital information such as medical history, allergies, and treatment plans. Also, placing 2D codes on medication labels provides detailed information about dosage, administration, and potential side effects.
Data Matrix codes are used to track pharmaceuticals through the supply chain, ensuring that drugs are genuine and have not been tampered with. This helps prevent counterfeit drugs from reaching patients.
Travel and transportation
Aztec codes and QR codes are commonly used on electronic boarding passes, allowing for quick and efficient check-in at airports. QR codes on train tickets enable fast entry and verification, reducing the need for physical ticket handling.
Education and training

Using QR codes in the classroom has many advantages. Placed in educational materials, they can link to additional resources, videos, or interactive exercises. Students who scan barcodes of the 2D type have easy access to training videos, manuals, and reference guides.
Also, QR codes in language learning textbooks can link to audio pronunciations of words and phrases, helping students practice and learn correct pronunciation.
Event management
QR codes for events can streamline the check-in processes by allowing attendees to scan codes from their tickets or digital passes. They can also provide information about event programs, schedules, and maps.
QR codes can be further used to control access to different areas of an event, such as VIP sections, backstage areas, or specific sessions. Scanning the code at entry points ensures that only authorized individuals can access restricted areas.
Personal and professional use
QR codes on business cards can store contact details, social media profiles, and websites, making it easy for professionals or workers to share and store critical contact information. The same codes can be used to quickly access and share documents, presentations, or portfolios.
What Are the Advantages of 2D Barcodes?
Higher storage capacity
Unlike 1D barcodes, which typically store up to 20 characters, 2D barcodes like QR codes and Data Matrix codes can hold hundreds to thousands of characters, including alphanumeric data, binary data, and special characters.
Versatility

They can encode various types of data, including numeric, alphanumeric, binary, and kanji characters, making them highly versatile for different applications.
2D barcodes store data in both horizontal and vertical dimensions, allowing for more complex and detailed information encoding compared to the single-dimensional structure of traditional barcodes.
Error correction
Many 2D barcode formats, such as QR codes, incorporate error correction capabilities. This means that even if part of the barcode is damaged or obscured, the encoded data can still be accurately read and reconstructed.
High-speed scanning
2D barcodes can be scanned quickly and easily from any angle, which enhances the speed and accuracy of data capture. Scanners and smartphones can read 2D barcodes with high efficiency, even if the barcode is partially damaged or oriented incorrectly.
Integration with mobile technology
You can scan QR codes using smartphones and tablets equipped with cameras. This integration makes them highly accessible for a wide range of users and applications, from accessing information to making transactions.
Cost-Effectiveness
The cost of printing 2D barcodes is relatively low, and they can be easily integrated into existing processes and systems without significant additional expenses.
Wrap-Up
2D barcodes are an absolute upgrade from 1D barcodes, in terms of sheer storage capacity, versatility, and use. With QR.io, you can generate customized QR codes that not only allow you to share a myriad of formats for many uses but also allow you to gain critical insights through QR code tracking.
Start your free trial now!
